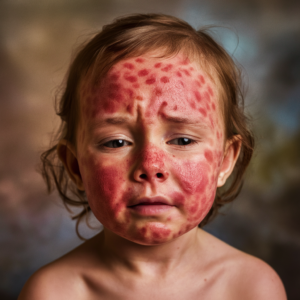
Introduction of chickenpox
The varicella-zoster virus is the highly transmitted virus that causes chickenpox (VZV).Although it mostly affects children under 10 years, adults who have not previously been exposed to the virus or had a vaccination against it may also contract it.
Symptoms of chickenpox
Constitutional symptoms are usually brief and mild (headache, fever, sore throat).
Rash
rash in crops at first on back then chest abdomen face and lastly limbs.
character: at first macule in a few hours dark pink papule which soon turns into a vesicle and within 24 hours into the pustule. the vesicles are elliptical or oval with axes parallel to the ribs.
Distribution:rash in more on upper arms and things upper part of face and in flexures.
Scab formation:pustules rupture and dry to form scab within 48 hours of appearance.
Pruritus,lymphadenopathy.
Complications
Direct viral effects
- pneumonia (usually adults or immunosuppressed )
- Myocarditis (usually adults or immunosuppressed )
post viral effects
- Encephalitis(cerebellar)
- Glomerulonephritis
Secondary becterial infection
- Skin
- septicemia
- osteomyelitis/septic arthritis
Intra-uterine infection
Congenital limb defects in rare case.
Management
- Bed rest
- For pruritus calamine lotion and antihistamine
- local antiseptic e.g chlorhexidine should be applied to the skin if there is secondary infection.
- Antibiotics- for secondary infection.
- Antiviral drugs: acyclovir (Zovirax 200mg) 800mg 5 time daily.